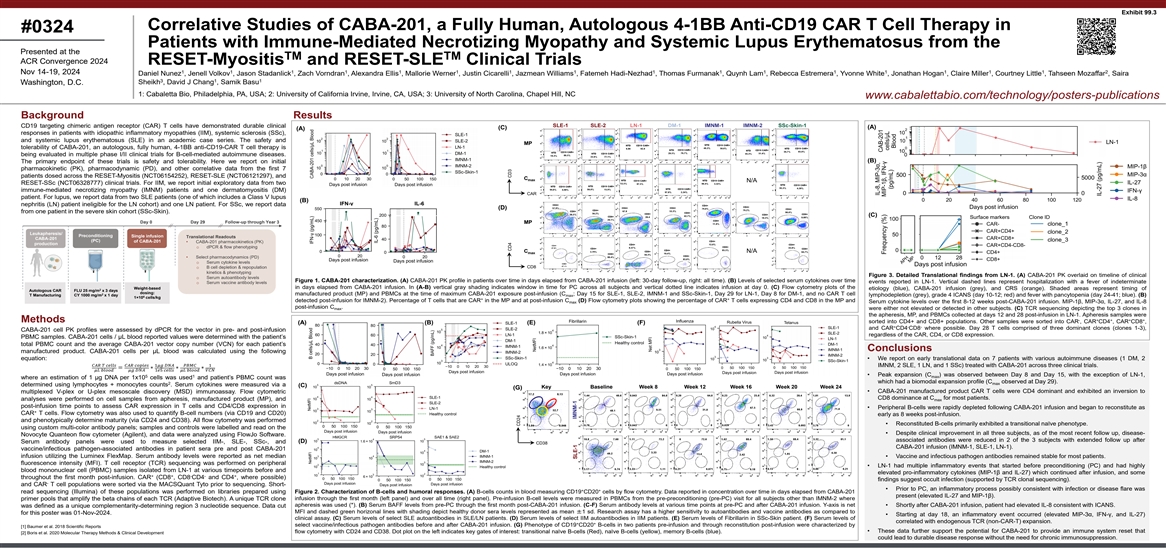

Exhibit 99.3 Correlative Studies of CABA-201, a Fully Human, Autologous 4-1BB Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy in #0324 Patients with Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from the Presented at the TM TM ACR Convergence 2024 RESET-Myositis and RESET-SLE Clinical Trials 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 Nov 14-19, 2024 Daniel Nunez , Jenell Volkov , Jason Stadanlick , Zach Vorndran , Alexandra Ellis , Mallorie Werner , Justin Cicarelli , Jazmean Williams , Fatemeh Hadi-Nezhad , Thomas Furmanak , Quynh Lam , Rebecca Estremera , Yvonne White , Jonathan Hogan , Claire Miller , Courtney Little , Tahseen Mozaffar , Saira 3 1 1 Sheikh , David J Chang , Samik Basu Washington, D.C. 1: Cabaletta Bio, Philadelphia, PA, USA; 2: University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA; 3: University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC www.cabalettabio.com/technology/posters-publications Background Results SLE-1 SLE-2 LN-1 DM-1 IMNM-1 IMNM-2 SSc-Skin-1 CD19 targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have demonstrated durable clinical (A) (C) (A) responses in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), systemic sclerosis (SSc), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in an academic case series. The safety and MP tolerability of CABA-201, an autologous, fully human, 4-1BB anti-CD19-CAR T cell therapy is being evaluated in multiple phase I/II clinical trials for B-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. (B) The primary endpoint of these trials is safety and tolerability. Here we report on initial pharmacokinetic (PK), pharmacodynamic (PD), and other correlative data from the first 7 patients dosed across the RESET-Myositis (NCT06154252), RESET-SLE (NCT06121297), and C max N/A RESET-SSc (NCT06328777) clinical trials. For IIM, we report initial exploratory data from two immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) patients and one dermatomyositis (DM) CAR patient. For lupus, we report data from two SLE patients (one of which includes a Class V lupus (B) IFN-γ IL-6 nephritis (LN) patient ineligible for the LN cohort) and one LN patient. For SSc, we report data (D) from one patient in the severe skin cohort (SSc-Skin). (C) Surface markers Clone ID Day 0 Day 29 Follow-up through Year 3 MP Leukapheresis/ Preconditioning Single infusion Translational Readouts CABA-201 (PC) of CABA-201 • CABA-201 pharmacokinetics (PK) production o dPCR & flow phenotyping C N/A max • Select pharmacodynamics (PD) o Serum cytokine levels CD8 o B cell depletion & repopulation kinetics & phenotyping Figure 3. Detailed Translational findings from LN-1. (A) CABA-201 PK overlaid on timeline of clinical o Serum autoantibody levels Figure 1. CABA-201 characterization. (A) CABA-201 PK profile in patients over time in days elapsed from CABA-201 infusion (left: 30-day follow-up, right: all time). (B) Levels of selected serum cytokines over time events reported in LN-1. Vertical dashed lines represent hospitalization with a fever of indeterminate o Serum vaccine antibody levels in days elapsed from CABA-201 infusion. In (A-B) vertical gray shading indicates window in time for PC across all subjects and vertical dotted line indicates infusion at day 0. (C) Flow cytometry plots of the Weight-based etiology (blue), CABA-201 infusion (grey), and CRS (orange). Shaded areas represent timing of 2 Autologous CAR FLU 25 mg/m x 3 days dosing: 2 manufactured product (MP) and PBMCs at the time of maximum CABA-201 exposure post-infusion (C ; Day 15 for SLE-1, SLE-2, IMNM-1 and SSc-Skin-1, Day 29 for LN-1, Day 8 for DM-1, and no CAR T cell T Manufacturing CY 1000 mg/m x 1 day max lymphodepletion (grey), grade 4 ICANS (day 10-12; red) and fever with pancytopenia (day 24-41; blue). (B) 6 1×10 cells/kg + + detected post-infusion for IMNM-2). Percentage of T cells that are CAR in the MP and at post-infusion C (D) Flow cytometry plots showing the percentage of CAR T cells expressing CD4 and CD8 in the MP and Serum cytokine levels over the first 8-12 weeks post-CABA-201 infusion. MIP-1β, MIP-3α, IL-27, and IL-8 max post-infusion C . max were either not elevated or detected in other subjects. (C) TCR sequencing depicting the top 3 clones in the apheresis, MP, and PBMCs collected at days 12 and 28 post-infusion in LN-1. Apheresis samples were - + + + + Methods sorted into CD4+ and CD8+ populations. Other samples were sorted into CAR , CAR CD4 , CAR CD8 , (A) (B) (E) (F) + - - and CAR CD4 CD8 where possible. Day 28 T cells comprised of three dominant clones (clones 1-3), CABA-201 cell PK profiles were assessed by dPCR for the vector in pre- and post-infusion regardless of the CAR, CD4, or CD8 expression. PBMC samples. CABA-201 cells / μL blood reported values were determined with the patient’s total PBMC count and the average CABA-201 vector copy number (VCN) for each patient’s Conclusions manufactured product. CABA-201 cells per μL blood was calculated using the following equation: • We report on early translational data on 7 patients with various autoimmune diseases (1 DM, 2 ���� ���� ������������������������ ����������������1�������� ����������������������������1 IMNM, 2 SLE, 1 LN, and 1 SSc) treated with CABA-201 across three clinical trials. =∗∗∗ �������� ���������������� ������������1������ ���������������������������� �������������������� • Peak expansion (C ) was observed between Day 8 and Day 15, with the exception of LN-1, 5 1 max where an estimation of 1 μg DNA per 1x10 cells was used and patient’s PBMC count was which had a biomodal expansion profile (C observed at Day 29). 2 max determined using lymphocytes + monocytes counts . Serum cytokines were measured via a (C) Key Baseline Week 8 Week 12 Week 16 Week 20 Week 24 (G) • CABA-201 manufactured product CAR T cells were CD4 dominant and exhibited an inversion to multiplexed V-plex or U-plex mesoscale discovery (MSD) immunoassay. Flow cytometric CD8 dominance at C for most patients. analyses were performed on cell samples from apheresis, manufactured product (MP), and max post-infusion time points to assess CAR expression in T cells and CD4/CD8 expression in • Peripheral B-cells were rapidly depleted following CABA-201 infusion and began to reconstitute as + CAR T cells. Flow cytometry was also used to quantify B-cell numbers (via CD19 and CD20) early as 8 weeks post-infusion. and phenotypically determine maturity (via CD24 and CD38). All flow cytometry was performed • Reconstituted B-cells primarily exhibited a transitional naïve phenotype. using custom multi-color antibody panels; samples and controls were labelled and read on the • Despite clinical improvement in all three subjects, as of the most recent follow up, disease- Novocyte Quanteon flow cytometer (Agilent), and data were analyzed using FlowJo Software. associated antibodies were reduced in 2 of the 3 subjects with extended follow up after (D) Serum antibody panels were used to measure selected IIM-, SLE-, SSc-, and CD38 CABA-201 infusion (IMNM-1, SLE-1, LN-1). vaccine/infectious pathogen-associated antibodies in patient sera pre and post CABA-201 infusion utilizing the Luminex FlexMap. Serum antibody levels were reported as net median • Vaccine and infectious pathogen antibodies remained stable for most patients. fluorescence intensity (MFI). T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing was performed on peripheral • LN-1 had multiple inflammatory events that started before preconditioning (PC) and had highly blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples isolated from LN-1 at various timepoints before and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines (MIP-1β and IL-27) which continued after infusion, and some + + - - + throughout the first month post-infusion. CAR (CD8 , CD8 CD4 and CD4 , where possible) findings suggest occult infection (supported by TCR clonal sequencing). - and CAR T cell populations were sorted via the MACSQuant Tyto prior to sequencing. Short- • Prior to PC, an inflammatory process possibly consistent with infection or disease flare was + + read sequencing (Illumina) of these populations was performed on libraries prepared using Figure 2. Characterization of B-cells and humoral responses. (A) B-cells counts in blood measuring CD19 CD20 cells by flow cytometry. Data reported in concentration over time in days elapsed from CABA-201 present (elevated IL-27 and MIP-1β). infusion through the first month (left panel) and over all time (right panel). Pre-infusion B-cell levels were measured in PBMCs from the pre-preconditioning (pre-PC) visit for all subjects other than IMNM-2 where primer pools that amplify the beta chains of each TCR (Adaptive Biotech). A unique TCR clone apheresis was used (*). (B) Serum BAFF levels from pre-PC through the first month post-CABA-201 infusion. (C-F) Serum antibody levels at various time points at pre-PC and after CABA-201 infusion. Y-axis is net • Shortly after CABA-201 infusion, patient had elevated IL-8 consistent with ICANS. was defined as a unique complementarity-determining region 3 nucleotide sequence. Data cut MFI and dashed green horizonal lines with shading depict healthy donor sera levels represented as mean ±1 sd. Research assay has a higher sensitivity to autoantibodies and vaccine antibodies as compared to for this poster was 01-Nov-2024. • Starting at day 18, an inflammatory event occurred (elevated MIP-3α, IFN-γ, and IL-27) clinical assay. (C) Serum levels of select SLE autoantibodies in SLE/LN patients. (D) Serum levels of select IIM autoantibodies in IIM patients. (E) Serum levels of Fibrillarin in SSc-Skin patient. (F) Serum levels of correlated with endogenous TCR (non-CAR-T) expansion. + + select vaccine/infectious pathogen antibodies before and after CABA-201 infusion. (G) Phenotype of CD19 CD20 B-cells in two patients pre-infusion and through reconstitution post-infusion were characterized by [1] Baumer et al. 2018 Scientific Reports • These data further support the potential for CABA-201 to provide an immune system reset that flow cytometry with CD24 and CD38. Dot plot on the left indicates key gates of interest: transitional naïve B-cells (Red), naïve B-cells (yellow), memory B-cells (blue). [2] Boris et al. 2020 Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development could lead to durable disease response without the need for chronic immunosuppression. CD4 CD3 CD24 IMNM-1 SLE-1 ������������������������ ������������������������